Worst States for Autism Services: A Comprehensive Analysis

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects millions of individuals and their families across the United States. Access to quality services is crucial for the development and well-being of individuals with autism. However, the availability and quality of these services vary significantly from state to state. In this post, we will explore some of the worst states for autism services, examine the factors contributing to their rankings, and examine the challenges faced by families living there.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Before delving into the analysis, it’s essential to understand Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). ASD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction. It also involves communication challenges and a tendency to engage in repetitive behaviors. The spectrum nature of autism means that it affects individuals differently and to varying degrees. Early intervention and access to appropriate services can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with autism.
Factors Influencing the Quality of Autism Services
Several factors influence the quality and availability of autism services in a state, including:
- Funding and Resources: State funding for autism services, including early intervention programs, educational support, and healthcare services.
- Legislation and Policies: State laws and policies that mandate insurance coverage for autism therapies and services.
- Availability of Specialists: Many trained professionals, such as developmental pediatricians, speech therapists, and occupational therapists, can provide autism-specific services.
- Access to Early Intervention: Early intervention programs are available. They can diagnose and support children with autism as early as possible.
- Educational Support: The quality of special education services in public schools, including Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and inclusion practices.
- Community Support and Awareness: The level of community support, awareness, and acceptance of individuals with autism.
The Worst States for Autism Services
Various reports, surveys, and expert analyses highlight certain states. These states are often cited as having some of the worst autism services in the United States.
1. Texas
Texas consistently ranks low in terms of autism services. Texas is one of the largest and most populous states. However, it faces significant challenges in providing adequate support for individuals with autism.
- Funding Issues: Texas has historically struggled with funding for special education and autism services. Budget cuts have reduced available resources and services.
- Insurance Coverage: While Texas mandates insurance coverage for autism therapies, the implementation and enforcement of these mandates are inconsistent. Families often face difficulties in obtaining necessary services through their insurance plans.
- Availability of Specialists: There is a shortage of autism specialists in Texas. This shortage makes it difficult for families to access timely and appropriate care.
2. Georgia
Georgia is another state where families of individuals with autism face significant challenges.
- Early Intervention: Access to early intervention services is limited, and many families report long waiting lists for evaluations and services.
- Educational Support: Special education services in Georgia are often criticized for being inadequate. Schools may lack the necessary resources and trained staff to support students with autism effectively.
- Community Awareness: There is a lack of community awareness. Support for individuals with autism is limited. This lack of support can lead to social isolation and discrimination.
3. Alabama
Alabama is known for its insufficient support and resources for individuals with autism.
- Funding: State funding for autism services is minimal, leading to a lack of available programs and resources.
- Legislation: Alabama has limited legislation mandating insurance coverage for autism services, leaving many families to pay out-of-pocket for essential therapies.
- Availability of Specialists: There is a significant shortage of trained autism specialists. This shortage results in long wait times for diagnosis and treatment.
4. Mississippi
Mississippi faces numerous challenges in providing adequate autism services to its residents.
- Early Intervention: Access to early intervention programs is limited, and families often face long service waiting periods.
- Educational Support: The quality of special education services in Mississippi is often criticized. These services are considered insufficient to meet the needs of students with autism.
- Healthcare Access: There is a lack of healthcare providers who specialize in autism. This makes it difficult for families to access necessary medical and therapeutic services.
5. West Virginia
West Virginia ranks low in terms of autism services due to several factors.
- Funding: The state provides limited funding for autism services, resulting in a lack of available resources and programs.
- Insurance Coverage: There is inadequate insurance coverage for autism therapies, and families often struggle to afford necessary treatments.
- Availability of Specialists: A shortage of trained professionals leads to long wait times for diagnosis and intervention.
Challenges Faced by Families
Families living in states with poor autism services face numerous challenges, including:
- Financial Burden: The cost of autism therapies and services can be overwhelming, especially in states with inadequate insurance coverage. Many families end up paying out-of-pocket for essential services.
- Long Wait Times: Due to the shortage of specialists and limited resources, families often face long waiting periods for diagnosis and treatment, which can delay critical early intervention.
- Inadequate Educational Support: In states with poor special education services, children with autism may not receive the support they need to succeed academically and socially.
- Social Isolation: The lack of community awareness and support can lead to social isolation and discrimination for individuals with autism and their families.
- Stress and Mental Health: The constant struggle to access necessary services and support can take a toll on the mental health and well-being of families.
Efforts to Improve Autism Services
Despite these challenges, ongoing efforts are being made to improve autism services across the United States. Advocacy groups, nonprofits, and community organizations work tirelessly to raise awareness, influence legislation, and support families.
- Advocacy and Legislation: Organizations such as Autism Speaks and the Autism Society of America advocate for better insurance coverage, increased funding, and improved access to services. They work with lawmakers to pass legislation that benefits individuals with autism.
- Community Programs: Various community programs and support groups provide resources, information, and emotional support to families affected by autism. These programs help build a sense of community and reduce social isolation.
- Training and Education: Efforts are being made to train more specialists in autism, including therapists, educators, and healthcare providers. Increased training ensures that more professionals are equipped to provide quality care.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing research into autism and its treatments is essential for developing new and effective therapies. Innovations in technology and healthcare can also improve access to services.
Comparison Table: Worst States for Autism Services
| Factor | Texas | Georgia | Alabama | Mississippi | West Virginia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Funding | Insufficient funding, budget cuts | Limited funding, resource constraints | Minimal state funding | Limited funding, resource constraints | Limited funding, resource constraints |
| Insurance Coverage | Inconsistent implementation | Insurance mandates in place but limited | Limited legislation for coverage | Inadequate insurance coverage | Inadequate insurance coverage |
| Availability of Specialists | Shortage of autism specialists | Shortage of trained professionals | Significant shortage | Shortage of specialists | Shortage of trained professionals |
| Early Intervention | Long wait times for services | Long waiting lists for evaluations | Limited access, long wait periods | Long waiting periods | Limited access, long wait times |
| Educational Support | Criticized for being inadequate | Inadequate special education resources | Insufficient support in schools | Poor quality special education | Criticized for insufficient support |
| Community Awareness | Limited community support and awareness | Lack of community awareness | Low community support and awareness | Low awareness and support | Low community awareness and support |
FAQ
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in social interaction, communication challenges, and repetitive behaviors. The severity and symptoms of ASD can vary widely among individuals, which is why it is referred to as a “spectrum.”
Why are some states worse for autism services than others?
The quality of autism services varies due to factors like state funding, insurance coverage mandates, availability of specialists, access to early intervention programs, quality of educational support, and community awareness. States that lack sufficient resources, supportive legislation, and trained professionals often provide lower-quality services.
Which states are considered the worst for autism services?
Based on various reports and analyses, Texas, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and West Virginia are often cited as having some of the worst autism services in the United States. These states struggle with funding, insurance coverage, availability of specialists, and other critical factors.
What are the main challenges faced by families in these states?
Families in states with poor autism services face several challenges, including financial burdens due to inadequate insurance coverage, long wait times for diagnosis and treatment, insufficient educational support, social isolation, and stress-related mental health issues.
How does inadequate funding affect autism services?
Inadequate funding leads to a lack of resources and programs necessary for supporting individuals with autism. This can result in limited access to early intervention programs, fewer trained specialists, and insufficient educational and therapeutic services.
What efforts are being made to improve autism services?
Several efforts are ongoing to improve autism services, including advocacy for better insurance coverage and increased funding, community programs providing resources and support, training and education for more specialists, and ongoing research and innovation in autism treatments.
What can families do to advocate for better autism services in their state?
Families can join advocacy groups, participate in community awareness programs, contact their local representatives to push for supportive legislation, and collaborate with local nonprofits to improve the availability and quality of autism services.
Are there any success stories of states improving their autism services?
Yes, some states have significantly improved their autism services through increased funding, better legislation, and community support initiatives. Sharing these success stories can provide a roadmap for other states looking to enhance their autism services.
How can communities support individuals with autism and their families?
Communities can support individuals with autism by promoting awareness and acceptance, providing inclusive programs and activities, offering support groups and resources for families, and advocating for better services and policies at the local and state levels.
Where can I find more information and resources on autism services?
For more information and resources, visit the websites of organizations such as Autism Speaks, the Autism Society of America, and local autism support groups. These organizations provide valuable information on services, advocacy, and support for individuals with autism and their families.
Conclusion
Access to quality autism services is crucial for the well-being and development of individuals with autism. Unfortunately, the availability and quality of these services vary significantly across the United States. States such as Texas, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and West Virginia face significant challenges in providing adequate support for individuals with autism.
Families living in these states often struggle with financial burdens, long wait times, inadequate educational support, social isolation, and mental health challenges. However, ongoing efforts by advocacy groups, community organizations, and researchers are working to improve autism services and support systems.
Policymakers, healthcare providers, educators, and communities need to prioritize the needs of individuals with autism and their families. By working together, we can ensure that everyone has access to the services and support they need to thrive, regardless of where they live.
Update: According to this Reedit post
- Northeast states like Massachusetts and Rhode Island are mentioned as having good facilities and support.
- Some suburbs of Chicago, particularly in the North Shore area, are praised for their excellent special education services.
- Colorado, especially the Colorado Springs area, is noted for having high ratings, although one user reported negative experiences.
- The Boston, MA area is repeatedly mentioned as having good resources and services.
- Some parts of Texas, particularly in the Dallas-Fort Worth (DFW) area, are said to have good school districts with strong special needs programs. Lewisville ISD, specifically schools in Flower Mound and Highland Village, are highlighted as being particularly good for autism support.
- California is expected to have similar facilities to the Northeast states.
- Connecticut is mentioned as having great special education programs, though housing costs are noted to be expensive.
- New York City is said to have good resources, but limited options for autistic children.
- Several users advise against Ohio, Florida, and Portland, Oregon due to poor experiences with special education services.
The importance of researching individual school districts is emphasized, as quality can vary significantly even within states known for good special education.
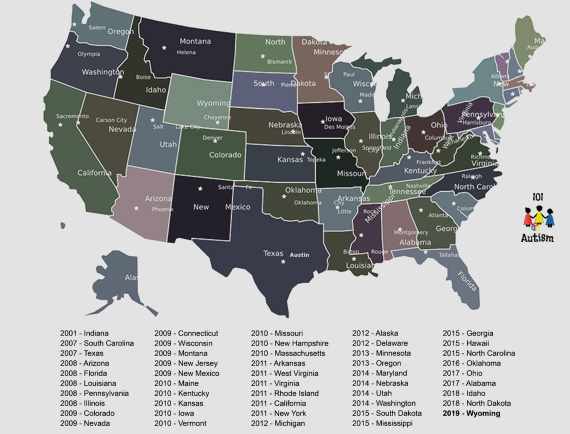
2011 State Autism Insurance Reform Initiative Map

Few private insurance companies or other employee benefit plans nationwide cover autism therapies. Most insurance companies designate autism as a diagnostic exclusion, meaning that no autism-specific services are covered. States (31) with enacted autism...
2023 Autism Insurance Reform Initiative map

Here are the data for the Autism Insurance Reform Initiative across different states in the United States. The data represents the number of individuals with a disability who have health insurance coverage. The data is divided into two age groups: under 19 years and 19 to 64 years. For each age group, the data is…
Autism Insurance Reform Initiative across different states in the United States 2023

Here are the data for the Autism Insurance Reform Initiative across different states in the United States. The data represents the number of individuals with a disability who have health insurance coverage. The data...
Discover more from Living with Autism
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




1 Response
[…] The Gateway Academy – Houston, Texas […]