
Early Signs of Autism in Children: Complete 2025 Guide for Parents
Last updated: May 8, 2025 | Reading time: 8 minutes | Medical review: Board-certified pediatricians
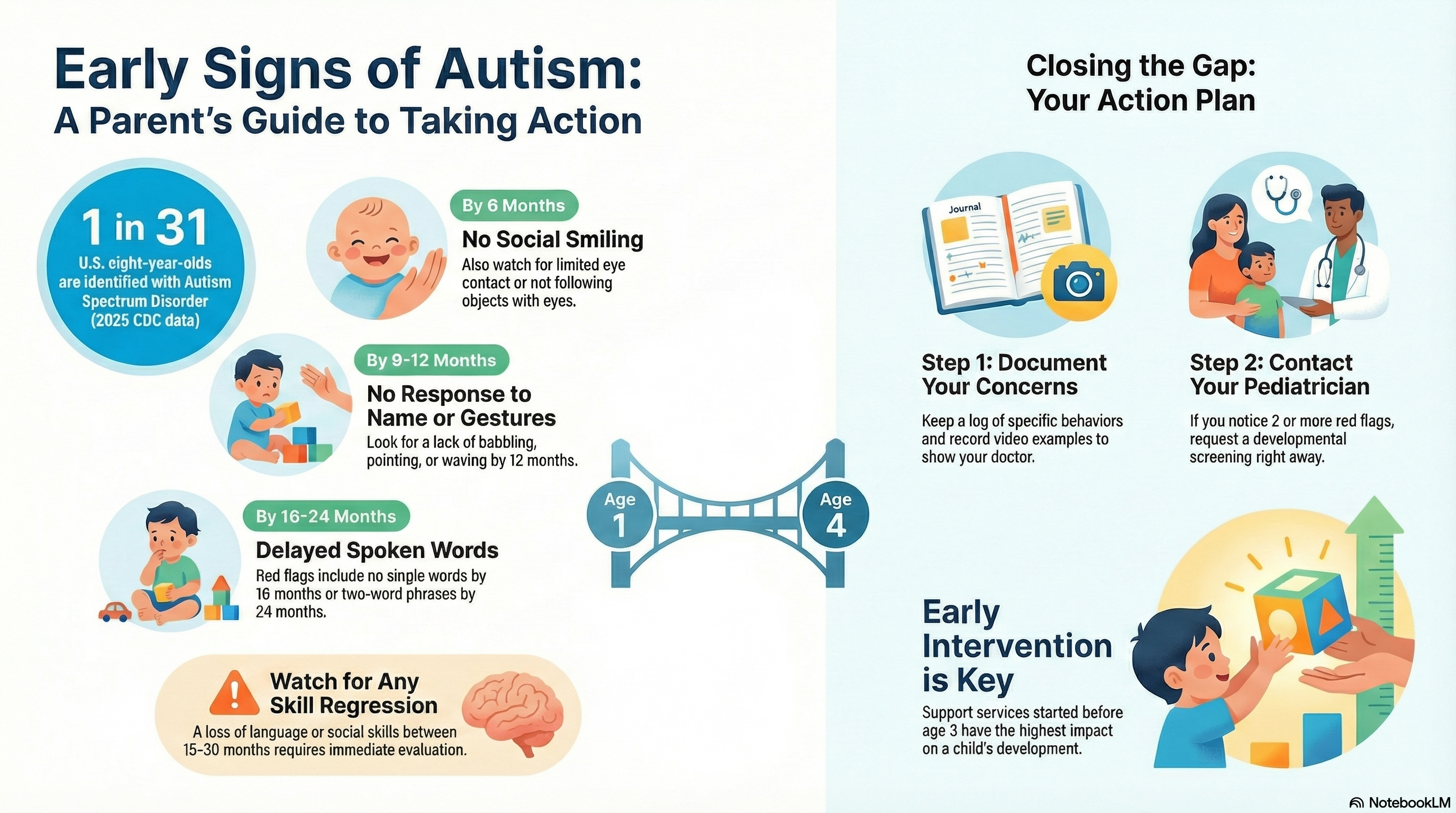
Quick take: About 1 in 31 (≈3.2%) eight‑year‑olds in the United States are now identified with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), according to the latest CDC ADDM Network report published in 2025. Early recognition of red flags—especially the subtle ones—remains the key to timely support.
🔍 TLDR – Key Takeaways
- 1 in 31 (3.2%) eight-year-olds in the US now have autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
- Early signs appear by 12 months, but average diagnosis age is still 4 years
- Girls often underdiagnosed – autism presents differently in females
- Key red flags: No social smiling by 6 months, no babbling by 12 months, regression of skills
- Action needed: If you notice 2+ signs, consult your pediatrician immediately
- Early intervention before age 3 shows the highest success rates
📋 Table of Contents
🎯 2025 Snapshot: Why Early Detection Matters
- Average age of diagnosis in the U.S. is still around 4 years, yet reliable signs can appear by 12 months.
- Diagnosis is over 3 times more common in boys, but researchers believe many girls remain undiagnosed until later childhood because their signs can look different.
- Early intervention services launched before age 3 show the highest impact on language and social outcomes.
- Brain plasticity is greatest in the first 3 years of life, making early support crucial.
- Cost-effectiveness: Early intervention reduces lifetime support needs and improves quality of life.
⚠️ Critical Timeline Gap
The Problem: While reliable autism signs can appear by 12 months, the average diagnosis age remains around 4 years. This 3-year gap represents missed opportunities for crucial early intervention that could significantly improve outcomes.
While these signs are common in children, it’s important to note that autism can present differently in girls. Being aware of the signs of autism in girls can help ensure early detection for all children.
👥 How Autism Presents Differently in Girls:
- Masking abilities: Girls may be better at copying social behaviors and hiding difficulties
- Different interests: Focus on horses, celebrities, or books instead of typical “male” interests
- Internalized struggles: Less obvious external behaviors, more internal anxiety and depression
- Social camouflaging: Better at mimicking social interactions but may struggle internally
- Late diagnosis: Often not identified until adolescence or adulthood
👶 Early Developmental Signs (0 – 12 Months)
Critical early indicators to watch for:
- Lack of social smiling by 6 months – Most babies smile socially by 2-3 months
- Limited eye contact or tendency to look past caregivers rather than at them
- Doesn’t respond to name by 9 months – Should turn head when called
- No babbling, pointing, or waving by 12 months – Key communication milestones
- Unusual reactions to sensory input (e.g., no startle at loud sounds or extreme distress at routine noises)
- Feeding difficulties – Extreme sensitivity to textures or temperatures
- Sleep disruptions – Persistent sleep issues beyond typical infant patterns
🚨 Immediate Concern Signs (0-12 months)
- No response to loud sounds by 3 months
- Doesn’t follow objects with eyes by 4 months
- No social smiling by 6 months
- No sitting without support by 9 months
- Extreme resistance to being held or cuddled
🧸 Signs in Toddlers (1 – 3 Years)
Critical developmental period – watch for:
- Delayed or absent spoken words (no single words by 16 months, no two-word phrases by 24 months)
- Phrases lost after previously acquired – Any regression in language or skills
- Repetitive motions (hand‑flapping, rocking, spinning, toe-walking)
- Strong need for routines; extreme distress at small changes in environment or schedule
- Fixated interests (e.g., spinning wheels, lining up toys, obsession with specific topics)
- Limited pretend play – Difficulty with make-believe or imaginative scenarios
- Parallel play only – Plays alongside but not with other children
- Difficulty with transitions – Meltdowns when activities or locations change
🎒 Indicators in Preschoolers (3 – 5 Years)
School readiness and social development concerns:
- Difficulty initiating or sustaining play with peers – Avoids group activities consistently
- Literal understanding of language; trouble with sarcasm, jokes, or make‑believe
- Preference for solitary activities – Consistently chooses to play alone
- Intense, niche interests (e.g., dinosaurs, train schedules, specific characters or topics)
- Persistent echolalia (repeating phrases verbatim without contextual understanding)
- Unusual speech patterns – Robotic tone, unusual pitch, rhythm, or volume
- Difficulty reading social cues – Missing facial expressions, body language, tone of voice
- Challenges with emotional regulation – Frequent meltdowns or emotional outbursts
⚠️ Watch for Regression
Roughly 20% of autistic children experience a loss of previously mastered words or social skills between 15 and 30 months. If regression occurs, seek a diagnostic evaluation right away.
🚨 Regression Warning Signs:
- Loss of spoken words previously used regularly
- Stops responding to name after previously doing so
- Decreased eye contact from previous levels
- Loss of social gestures (waving, pointing, clapping)
- Withdrawal from social interaction – becomes more isolated
- Loss of play skills – stops engaging with toys appropriately
If any regression occurs, seek a diagnostic evaluation immediately. Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference.
🎭 Sensory Differences to Notice
Sensory processing differences are present in up to 95% of children with autism:
- Extreme sensitivities to textures (clothing tags, food textures), lights (fluorescent, bright), or sounds (vacuum, hand dryers)
- Unusual fascination with spinning objects, lights, fans, or reflective surfaces
- Pain tolerance extremes – Either very high or very low sensitivity to pain, temperature, or physical discomfort
- Seeking sensory input – Excessive spinning, jumping, crashing into things
- Avoiding sensory input – Covering ears, hiding from lights, refusing certain textures
- Oral sensitivities – Extremely limited diet, gagging on textures, or excessive mouthing of objects
🏥 When to Seek a Professional Evaluation
Immediate action recommended if you notice:
- Two or more red flags from any of the sections above
- Any regression of previously acquired skills at any age
- Missed major developmental milestones (see specific ages listed above)
- Persistent concerns about your child’s development, even if subtle
- Daycare or preschool expressing concerns about social or communication development
- Family history of autism or related developmental conditions
📋 Your Action Checklist:
- Document specific behaviors – Keep a log with dates and examples
- Record video examples – Show healthcare providers specific concerns
- Contact your pediatrician – Request developmental screening
- Complete validated screening tools – M-CHAT-R, ASQ, or similar assessments
- Gather family developmental history – Note any delays or diagnoses in relatives
- Research local early intervention services – Know your options before you need them
You can also review our guide on who can diagnose autism and our 2025 autism testing FAQ to prepare.
🚀 Early Intervention & Support Options (2025)
Evidence‑based therapies—ABA, speech‑language therapy, and occupational therapy—yield the best outcomes when started by age 3. Research consistently shows that intensive early intervention can lead to significant improvements in communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors.
🎯 Most Effective Evidence-Based Interventions:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Structured teaching method that breaks down skills into small steps
- Early Start Denver Model (ESDM): Play-based intervention for children 12-48 months
- Speech-Language Therapy: Develops communication skills, from nonverbal to complex language
- Occupational Therapy: Addresses sensory processing, motor skills, and daily living activities
- Social Skills Training: Structured programs to teach peer interaction and friendship skills
- Parent Training Programs: Teaching families how to support development at home
Explore our detailed breakdown of parent‑focused treatment options for practical steps.
❓ Quick FAQ (2025)
What are the very first signs of autism in babies?
The earliest signs include lack of social smiling by 6 months, limited eye contact, not responding to their name by 9 months, and no babbling, pointing, or waving by 12 months. Some babies may also show unusual reactions to sensory input, such as not startling at loud sounds or being extremely distressed by normal household noises.
Can autism be detected at 6 months?
While a formal diagnosis typically isn’t made until 18-24 months or later, some early warning signs like lack of social smiling, limited eye contact, and unusual sensory responses can be noticed by 6 months. Early screening and monitoring are important even if diagnosis comes later, as early intervention can begin before formal diagnosis.
Is autism the same as ADHD?
No. While some traits overlap, ASD involves differences in social communication and restricted interests. Learn how to tell them apart in our article on autism vs. ADHD. However, it’s important to note that some children can have both conditions simultaneously.
Does vaccination cause autism?
No credible scientific evidence supports a causal link between vaccines and autism. Multiple large‑scale studies involving millions of children confirm vaccine safety. The timing of autism signs appearing often coincides with vaccination schedules, but this is correlation, not causation.
What are the latest prevalence numbers?
The CDC’s 2025 ADDM Network report puts U.S. prevalence at 1 in 31 eight‑year‑olds, representing a significant increase from previous estimates. This increase is largely attributed to improved awareness, better diagnostic tools, and expanded understanding of the autism spectrum.
How early can autism intervention start?
Early intervention can begin as soon as developmental concerns are identified, even before formal diagnosis. Many states offer Early Intervention services for children under 3 who show developmental delays or are at risk. Research consistently shows the greatest benefits when comprehensive support starts before age 3, during the period of highest brain plasticity.
What should I do if my child shows regression?
Any loss of previously acquired skills (language, social, or motor) should be evaluated immediately. Contact your pediatrician right away and request an urgent developmental assessment. Regression can occur in about 20% of children with autism, typically between 15-30 months, and early intervention after regression can help recovery.
Quick Reference: Age-Based Autism Red Flags
- 6 months: No social smiling, limited eye contact
- 9 months: Doesn’t respond to name, no pointing or gesturing
- 12 months: No babbling, waving, or first words
- 16 months: No single words or loss of previously acquired language
- 24 months: No two-word phrases, repetitive behaviors emerge
- 3+ years: Difficulty with peer play, literal language understanding
Emergency Signs – Seek Immediate Evaluation:
- Any loss of previously acquired skills (regression)
- Complete lack of eye contact by 6 months
- No response to name by 12 months
- No words by 16 months
- Extreme sensory reactions affecting daily functioning
Comprehensive FAQ Section – What Parents Most Want to Know:
What is autism?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. It’s called a “spectrum” because symptoms and abilities vary widely from person to person. Some individuals with autism may need significant daily support, while others live independently and have successful careers.
What are the main signs of autism in children?
The primary signs fall into two main categories:
- Social Communication Challenges: Difficulty with eye contact, facial expressions, sharing interests, understanding social cues, developing peer relationships appropriate to developmental level
- Restricted and Repetitive Behaviors: Repetitive motor movements, insistence on routines, highly focused special interests, sensory sensitivities (over- or under-responsiveness)
At what age should I be concerned about my child’s development?
While every child develops at their own pace, certain milestones should prompt immediate evaluation:
- No social smiling by 6 months
- No babbling or pointing by 12 months
- No single words by 16 months
- No two-word phrases by 24 months
- Loss of any previously acquired skills at any age
Trust your parental instincts – if something seems “off” about your child’s development, seek professional evaluation.
What should I do if I think my child may have autism?
If you suspect your child may have autism, take these immediate steps:
- Document your concerns: Keep a detailed log of specific behaviors, when they occur, and their frequency
- Contact your pediatrician: Request a developmental screening and discuss your specific concerns
- Complete screening tools: Use validated assessments like the M-CHAT-R
- Seek specialist evaluation: Developmental pediatricians, child psychologists, or autism specialists can provide comprehensive assessment
- Don’t wait: Early intervention services can begin even before formal diagnosis
What are the most effective treatments for autism?
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for autism, but several evidence-based interventions show strong results when started early:
- Early Intensive Behavioral Intervention: Comprehensive programs providing 20-40 hours per week of structured teaching
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Evidence-based therapy that breaks down skills into teachable components
- Speech-Language Therapy: Develops communication skills from basic gestures to complex conversation
- Occupational Therapy: Addresses sensory processing issues and develops daily living skills
- Social Skills Training: Structured programs to teach peer interaction and friendship skills
How can I best support my child with autism?
Supporting a child with autism requires a comprehensive, family-centered approach:
- Educate yourself thoroughly: Learn about autism, evidence-based interventions, and your child’s specific needs and strengths
- Create a supportive home environment: Establish predictable routines, sensory-friendly spaces, and clear expectations
- Advocate for appropriate education: Work with schools to develop an Individualized Education Program (IEP) or 504 plan
- Build a support network: Connect with other families, join support groups, and work with a coordinated team of professionals
- Focus on your child’s strengths: Many children with autism have exceptional abilities in specific areas – nurture these talents
- Take care of yourself: Parenting a child with autism can be challenging – ensure you have support and respite
Remember that with appropriate support and intervention, children with autism can learn, grow, and thrive. Many individuals with autism lead fulfilling, independent lives and make significant contributions to their communities.
If you have additional questions or concerns about autism, consult with your pediatrician. You can also reach out to a developmental specialist or other qualified healthcare providers. They can provide personalized guidance based on your child’s specific needs.
💬 Social & Communication Red Flags
Communication and social interaction challenges: